어노테이션 기반의 캐시를 종종 애용해주시는 우기님 덕분에 공부를 하게 되었다.
기회를 제공한 우기님께 감사를 드립니다.
@Cacheable 어노테이션이 붙어 있는 메서드를 호출하게 되면 어떤 과정이 수행되어 캐시에 데이터가 저장되고 하는지가 궁금했다.
현상에 대한 디버깅을 통해 분석한 것이라 여러 방법 중에 하나일 수 있다.
디버깅을 하다보면 CacheInterceptor 클래스가 보이는데 아래와 같은 계층 구조로 되어 있다.
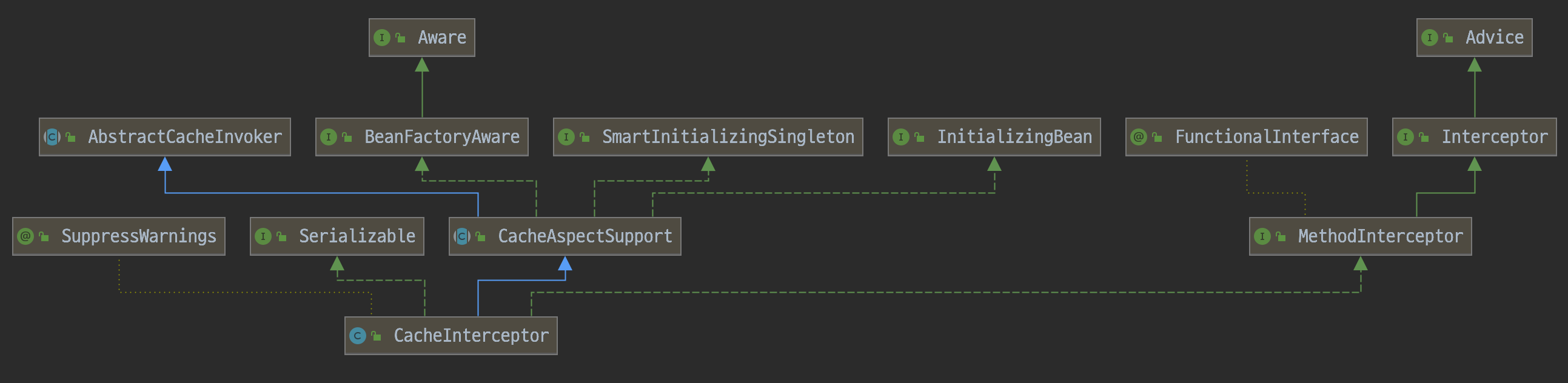
아래와 같은 MethodInterceptor 인터페이스를 구현하고 있기에 존재하는 메서드는 invoke 메서드 하나 뿐이다.
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MethodInterceptor extends Interceptor {
Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable;
}중간에 CacheAspectSupport 라는 추상 클래스가 존재하는데 이 클래스에 많은 메서드들이 있다.
캐시의 주요 기능이 값이 있으면 캐싱된 값을 돌려주고, 없으면 원천 소스에서 값을 찾아 캐시에 저장하고 돌려주는 것인데 이 기능이 execute 메서드에 있었다.
package org.springframework.cache.interceptor;
public abstract class CacheAspectSupport extends AbstractCacheInvoker
implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean, SmartInitializingSingleton {
// ..
@Nullable
protected Object execute(CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Object target, Method method, Object[] args) {
// Check whether aspect is enabled (to cope with cases where the AJ is pulled in automatically)
if (this.initialized) {
Class<?> targetClass = getTargetClass(target);
CacheOperationSource cacheOperationSource = getCacheOperationSource();
if (cacheOperationSource != null) {
Collection<CacheOperation> operations = cacheOperationSource.getCacheOperations(method, targetClass);
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(operations)) {
return execute(invoker, method,
new CacheOperationContexts(operations, method, args, target, targetClass));
}
}
}
return invoker.invoke();
}
사실 위의 메서드는 실행의 준비 단계이고 실제 수행은 3중 if 에 있는 execute이다.
package org.springframework.cache.interceptor;
public abstract class CacheAspectSupport extends AbstractCacheInvoker
implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean, SmartInitializingSingleton {
// ..
@Nullable
private Object execute(final CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Method method, CacheOperationContexts contexts) {
// Special handling of synchronized invocation
if (contexts.isSynchronized()) {
CacheOperationContext context = contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class).iterator().next();
if (isConditionPassing(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT)) {
Object key = generateKey(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
Cache cache = context.getCaches().iterator().next();
try {
return wrapCacheValue(method, cache.get(key, () -> unwrapReturnValue(invokeOperation(invoker))));
}
catch (Cache.ValueRetrievalException ex) {
// The invoker wraps any Throwable in a ThrowableWrapper instance so we
// can just make sure that one bubbles up the stack.
throw (CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper) ex.getCause();
}
}
else {
// No caching required, only call the underlying method
return invokeOperation(invoker);
}
}
// Process any early evictions
processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), true,
CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
// Check if we have a cached item matching the conditions
Cache.ValueWrapper cacheHit = findCachedItem(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class));
// Collect puts from any @Cacheable miss, if no cached item is found
List<CachePutRequest> cachePutRequests = new LinkedList<>();
if (cacheHit == null) {
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class),
CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT, cachePutRequests);
}
Object cacheValue;
Object returnValue;
if (cacheHit != null && !hasCachePut(contexts)) {
// If there are no put requests, just use the cache hit
cacheValue = cacheHit.get();
returnValue = wrapCacheValue(method, cacheValue);
}
else {
// Invoke the method if we don't have a cache hit
returnValue = invokeOperation(invoker);
cacheValue = unwrapReturnValue(returnValue);
}
// Collect any explicit @CachePuts
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CachePutOperation.class), cacheValue, cachePutRequests);
// Process any collected put requests, either from @CachePut or a @Cacheable miss
for (CachePutRequest cachePutRequest : cachePutRequests) {
cachePutRequest.apply(cacheValue);
}
// Process any late evictions
processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), false, cacheValue);
return returnValue;
}
캐시를 찾는 작업이면 중간에 findCachedItem 메서드를 호출하여 결과(cacheHit)가 null 일 경우에는 collectPutRequests 를 수행하고,
있으면 해당 값을 돌려주게 되는 것이었다.
그래서 아래와 같은 CALL stack 이 만들어진다.

execute: 435, CacheAspectSupport (org. springframework.cache.interceptor) <-
execute: 345, CacheAspectSupport (org. springframework.cache.interceptor)
invoke:61, Cachelnterceptor (org.springframework.cache.interceptor)
proceed: 186, ReflectiveMethodInvocation (org.springframework.aop.framework)
intercept:688, CglibAopProxy$DynamicAdvisedInterceptor (org.springframework.aop.framework)
'Programing > Framework' 카테고리의 다른 글
| spring-boot 신규 프로젝트 BY spring initializr (0) | 2021.04.28 |
|---|---|
| [스프링] MVC - @RequestBody 객체의 Setter가 필요한가? (2) | 2021.04.26 |
| [spring] JSR-303 과 @Valid 과 @Validated (0) | 2020.11.11 |
| [spring] URL path template에서 매핑된 값 구하기 (0) | 2020.11.11 |
| [spring] ServletWebRequest 생성 (0) | 2020.11.11 |



